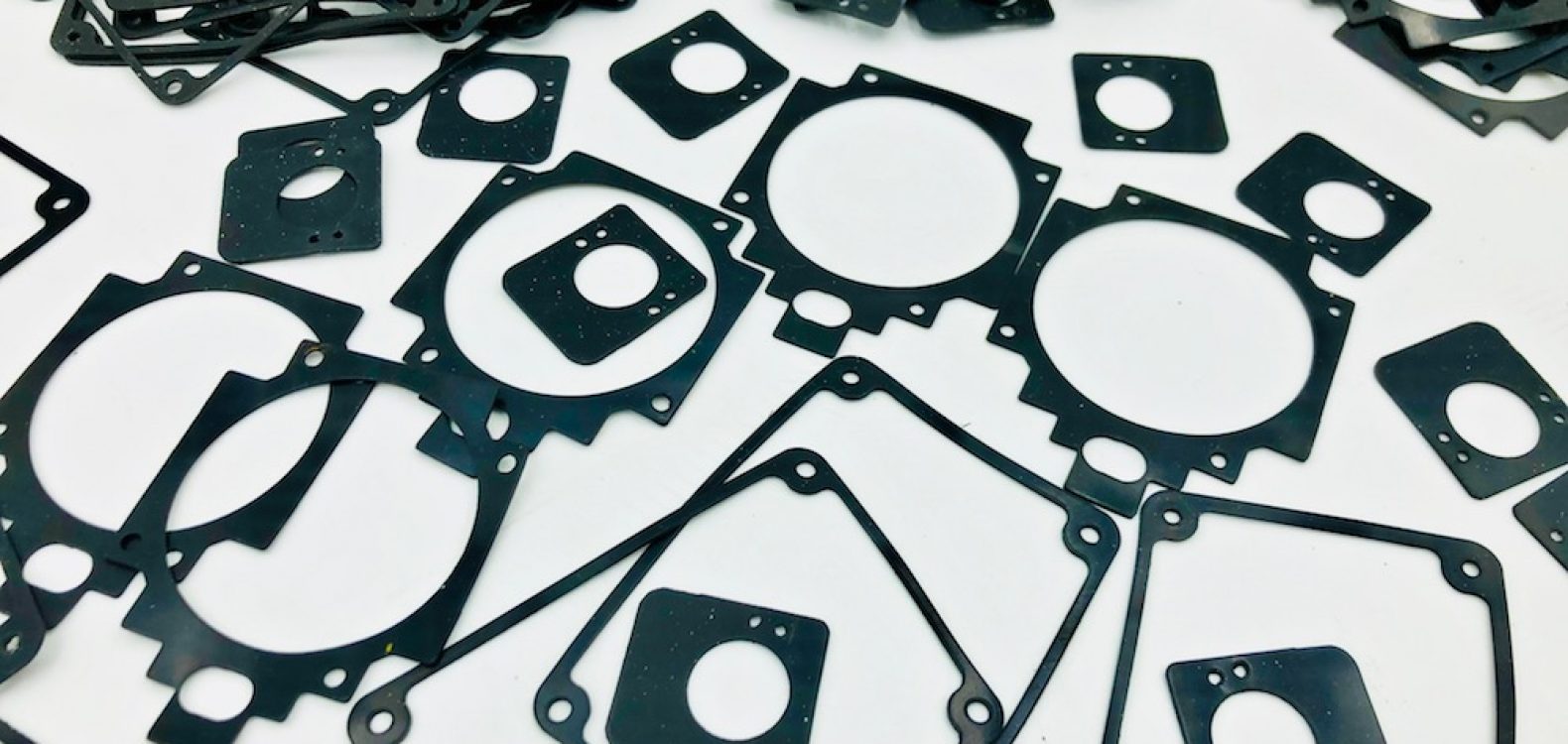
Dilatation seals, often referred to as expansion joints or expansion bellows, are vital components in various engineering and construction applications. These specialized devices serve the critical purpose of accommodating movement and expansion within structures, systems, or machinery while maintaining a seal or barrier to prevent the ingress of unwanted elements like dust, water, or gases. The term “dilatation” is often used in this context to describe the expansion or contraction of materials and components in response to changes in temperature, pressure, or mechanical stress.
Here’s a comprehensive overview of dilatation seals, their functions, types, and applications:
1. Function of Dilatation Seals:
Dilatation seals are primarily designed to address the following key functions:
A. Accommodating Thermal Expansion: One of the most common applications of dilatation seals is to allow for the thermal expansion and contraction of materials. When subjected to temperature variations, materials naturally expand or contract, and these seals help to absorb the resulting dimensional changes, thus preventing structural damage or system failure.
B. Absorbing Vibration and Movement: In various industrial and mechanical systems, there can be dynamic movements and vibrations. Dilatation seals help to absorb and isolate these vibrations, protecting the integrity of the connected components and reducing the risk of wear and tear.
C. Sealing and Isolating: Dilatation seals are used to create a barrier or seal between two components or sections of a system. This sealing function is essential to prevent the leakage of fluids, gases, or other substances from one part to another.
2. Types of Dilatation Seals:
There are several types of dilatation seals designed to suit specific applications. Some common types include:
A. Metallic Expansion Joints: These are made of various metals like stainless steel and are used in high-temperature and high-pressure applications, such as in power plants, chemical processing, and pipelines.
B. Rubber Expansion Joints: Rubber expansion joints are used in applications where flexibility and vibration absorption are important. They are commonly used in HVAC systems, water treatment facilities, and industrial equipment.
C. Fabric Expansion Joints: Fabric expansion joints are constructed from layers of specialized fabric materials and are used in applications that require flexibility, such as ducting systems in industrial processes.
D. Elastomeric Expansion Joints: These are designed to accommodate small to moderate movements and are often used in plumbing and HVAC systems.
E. PTFE Expansion Joints: Made of polytetrafluoroethylene, these expansion joints are highly resistant to chemicals and are used in chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
3. Applications:
Dilatation seals find application in a wide range of industries and systems, including:
A. Pipelines: To absorb movement and vibration in pipelines for fluids, gases, and steam.
B. HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to isolate vibrations and accommodate thermal expansion.
C. Power Plants: In high-temperature and high-pressure environments to absorb thermal expansion and vibrations in exhaust systems, ductwork, and more.
D. Chemical Processing: To seal and accommodate movement in chemical reactors and pipelines.
E. Transportation: In bridges and roads to absorb movement due to traffic and temperature changes.
F. Industrial Machinery: In various manufacturing equipment to absorb vibrations and movement.
In summary, dilatation seals are indispensable components in engineering and construction, playing a critical role in maintaining the structural integrity of systems, preventing leaks, and ensuring the longevity and reliability of various applications across multiple industries. The choice of the right type of dilatation seal depends on the specific requirements and operating conditions of the system or structure in question.